Introduction:
Field Workforce Management Software is a tool designed to help businesses manage their employees working outside the office. This software assists in scheduling, tracking, and communicating with field workers, ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and on time. It is essential for businesses that rely on field operations, such as utilities, repair and maintenance, installation, healthcare, construction and many more.
Moreover, this software provides valuable insights through data analytics, allowing managers to make informed decisions and continuously improve their operations. By leveraging real-time data, businesses can identify patterns, forecast future needs, and respond proactively to any issues that arise. This not only boosts operational efficiency but also enhances overall service quality, leading to increased customer satisfaction and a competitive edge in the market.
Importance in Modern Business Operations
In today's fast-paced world, efficient management of field workers is crucial for maintaining high productivity and customer satisfaction. Field Workforce Management Software helps businesses streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve service quality.
Additionally, by automating routine tasks such as scheduling, dispatching, and reporting, this software frees up time for managers and field workers to focus on more strategic activities. It also enhances transparency and accountability by providing a clear record of all field operations, which can be invaluable for performance evaluations and regulatory compliance. Ultimately, adopting Field Workforce Management Software empowers businesses to operate more effectively and deliver superior service to their clients.
Brief History and Evolution
Initially, managing field workers involved manual processes and paperwork. With the advent of technology, software solutions emerged to automate these tasks, making management more efficient and less error-prone. Over time, these solutions have evolved to include advanced features like GPS tracking, mobile access, and real-time updates.
Furthermore, the integration of cloud-based platforms has revolutionized field workforce management by enabling seamless data access and synchronization across multiple devices and locations. This ensures that all stakeholders have up-to-date information at their fingertips, facilitating better coordination and faster decision-making. As a result, businesses can respond more swiftly to changes and unforeseen challenges, maintaining a high level of operational efficiency.
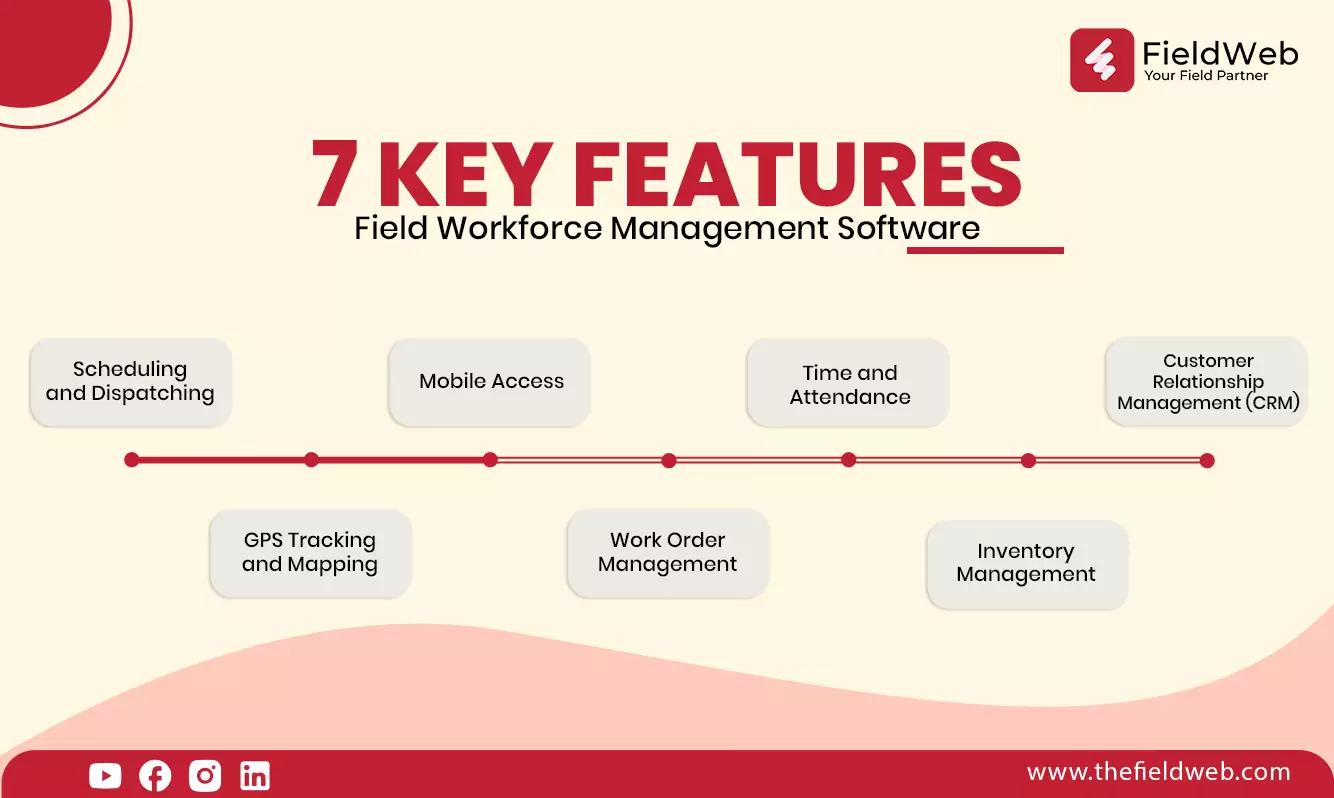
Key Features
1. Scheduling and Dispatching
Automated scheduling helps businesses assign tasks to the right workers based on their skills and availability, ensuring that each job is matched with the most qualified personnel. Real-time updates and notifications ensure that everyone stays informed about changes in the schedule, reducing the risk of miscommunication and delays. This feature also allows for dynamic rescheduling, so managers can quickly adjust plans to accommodate urgent tasks or unexpected changes in availability.
2. GPS Tracking and Mapping
Real-time location tracking allows managers to see where their field workers are at any moment, enhancing oversight and security. Route optimization helps in reducing travel time and fuel costs by calculating the most efficient paths for workers to take, ensuring they reach their destinations quickly and efficiently. This feature not only saves time and money but also minimizes wear and tear on vehicles, contributing to longer fleet lifespans and lower maintenance costs.
3. Mobile Access
Effective communication is key to successful service delivery. HVAC scheduling software provides robust communication tools, enabling technicians to stay in constant contact with dispatchers, colleagues, and customers throughout the service lifecycle.
4. Work Order Management
This feature allows managers to create, assign, and track work orders, providing a clear workflow for each task. Workers can update the status of their tasks, ensuring that everyone stays informed about the progress and any issues that may arise. This transparency helps in prioritizing tasks, avoiding overlaps, and ensuring that deadlines are met. Additionally, it provides a historical record of all work orders, which can be useful for performance reviews and audits.
5. Time and Attendance
Accurate time tracking helps businesses manage payroll and ensure that workers are paid for their actual hours worked. Integration with payroll systems simplifies the process by automating the transfer of time data, reducing errors and administrative workload. This feature also supports compliance with labor regulations by maintaining precise records of working hours, breaks, and overtime, thereby protecting both the business and its employees.
6. Inventory Management
Keeping track of inventory levels is crucial for field operations, ensuring that necessary materials and equipment are always available when needed. The software alerts managers when stock is low, prompting timely reorders and preventing delays due to shortages. This feature also allows for tracking the usage of inventory items, providing insights into consumption patterns and helping in better forecasting and budgeting.
7. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Managing customer information and communication is vital for providing excellent service and building long-term relationships. The CRM features help businesses keep track of customer interactions, preferences, and feedback, improving overall satisfaction. This information can be used to personalize service, address issues promptly, and identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling, thereby enhancing customer loyalty and driving revenue growth.
Benefits
1. Increased Worker Productivity
Field Workforce Management Software streamlines workflows by automating routine tasks and optimizing schedules, allowing field workers to focus more on their core responsibilities. With real-time access to task details and seamless communication with the office, workers can complete more tasks in less time. This increase in productivity not only enhances operational efficiency but also boosts employee morale as they can work more effectively without unnecessary interruptions or delays.
2. Increased Customer Satisfaction and Reduced Churn Rate
The software helps businesses respond more quickly and efficiently to customer needs, leading to higher satisfaction levels. Features like real-time updates and accurate scheduling ensure that services are delivered promptly and reliably. Happier customers are less likely to switch to competitors, reducing churn rates. By maintaining strong relationships and consistently meeting customer expectations, businesses can foster loyalty and trust, leading to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
3. Increased Monthly Revenue
Efficient management of field operations translates to more tasks completed in less time, directly contributing to increased monthly revenue. By minimizing downtime and maximizing productive hours, businesses can handle more jobs and serve more customers. Additionally, the insights gained from performance analytics enable managers to identify new revenue opportunities, such as upselling services or optimizing pricing strategies, further boosting monthly income.
4. Decrease in Opportunity Loss and Expense Leakages
Field Workforce Management Software helps businesses minimize opportunity loss by ensuring that no job is overlooked or delayed. Automated scheduling and dispatching mean that tasks are assigned promptly and accurately, preventing missed opportunities. Furthermore, the software's inventory management and time tracking features help identify and eliminate expense leakages by ensuring that resources are used efficiently and that all billable hours are accurately recorded. This leads to better financial management and a healthier bottom line.
Implementation Considerations
1. Choosing the Right Software
When selecting Field Workforce Management Software, consider factors like scalability, ease of use, and available features. It is crucial to choose a solution that can grow with your business, accommodating an increasing number of users and expanding functionalities as needed. User-friendly interfaces reduce the learning curve for your team, ensuring quicker adoption and effective utilization. Compare popular options by examining customer reviews, requesting demos, and evaluating trial versions to find the one that best suits your business needs. Additionally, consider the software provider's reputation, the level of customer support they offer, and any long-term costs associated with the software.
2. All-in-One Software
Opting for an all-in-one software solution can simplify your operations by consolidating multiple functionalities into a single platform. This approach eliminates the need for juggling various tools and ensures that all aspects of field workforce management—scheduling, dispatching, GPS tracking, CRM, and more—are seamlessly integrated. An all-in-one solution reduces the complexity of managing disparate systems and enhances data accuracy by maintaining a single source of truth. This integration leads to more efficient workflows, better coordination among teams, and ultimately, a more streamlined operation. Ensure that the chosen software is flexible and customizable to cater to the specific needs of your business.
3. Training and Support
Proper training is essential for field workers to use the software effectively. Choose a provider that offers comprehensive training programs, including initial onboarding sessions, ongoing educational resources, and access to a knowledge base. Training should be tailored to different user roles within your organization, ensuring that everyone from managers to field workers understands how to leverage the software's capabilities. Reliable customer support is equally important; look for providers that offer multiple support channels such as phone, email, and live chat, along with prompt response times. Effective training and support help maximize the return on your investment by ensuring that your team can fully utilize the software to enhance productivity and efficiency.
Challenges in Software Adoption
Adopting software in the service industry can bring significant benefits, but it also comes with several challenges. Here are the major challenges:
1. Resistance to Change
- Employee Reluctance: Employees may fear the unknown when faced with new software, worrying about their ability to adapt or the impact on their roles. Clear communication about the benefits and support during the transition can alleviate these concerns.
- Cultural Barriers: Some company cultures may resist technological changes, preferring traditional methods. Overcoming cultural resistance requires strong leadership, effective change management strategies, and demonstrating the positive impact of the software on the company's goals and values.
2. Training and Skill Gaps
- Learning Curve: Employees need time and resources to familiarize themselves with new software, which can temporarily affect productivity. Providing comprehensive training programs, tutorials, and ongoing support can help reduce the learning curve and boost confidence.
- Skill Deficiency: Not all employees may possess the technical skills required to use the software efficiently. Offering targeted training sessions, mentorship programs, or hiring new staff with the necessary expertise can address skill gaps and ensure smooth adoption.
3. Cost and Budget Constraints
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost of purchasing, implementing, and customizing new software can strain the company's budget. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis and exploring flexible payment options, such as leasing or financing, can make the investment more manageable.
- Ongoing Costs: Maintenance, updates, and subscription fees can add to the total cost of ownership over time. Budgeting for these recurring expenses and negotiating favorable terms with the software vendor can help mitigate financial strain.
4. Integration Issues
- Compatibility: Ensuring seamless integration with existing systems and tools is crucial for maintaining workflow continuity. Collaboration between IT teams and software providers, rigorous testing, and implementing interoperability standards can help overcome compatibility challenges.
- Data Migration: Transferring data from legacy systems to new software requires careful planning and execution to prevent data loss or corruption. Establishing data migration protocols, conducting thorough data audits, and engaging experienced data migration specialists can ensure a smooth transition.
5. Data Security Concerns
- Privacy Risks: Storing sensitive customer and business data in new software systems raises concerns about data privacy and security. Implementing robust encryption, access controls, and compliance with relevant regulations can safeguard sensitive information and build trust with customers.
- Compliance: Ensuring that the software complies with industry regulations and standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is critical to avoid legal liabilities and penalties. Regular audits, adherence to security best practices, and staying informed about evolving regulations are essential for maintaining compliance.
6. Customization and Flexibility
- Unique Requirements: Service industries often have specific workflows and processes that off-the-shelf software may not fully address. Investing in customizable solutions or partnering with vendors who offer extensive customization options can tailor the software to meet the company's unique needs.
- Scalability: As the business grows, the software must be able to scale to accommodate increased workloads and additional users without sacrificing performance. Choosing scalable solutions, regularly reviewing system capacity, and investing in infrastructure upgrades as needed can ensure smooth scalability.
7. Downtime and Disruption
- Implementation Period: The process of implementing new software can disrupt regular business operations, leading to downtime and productivity losses. Careful planning, phased rollout strategies, and providing alternative workflows during implementation can minimize disruptions and maintain business continuity.
- Technical Glitches: Initial bugs and issues with the software can hinder its effectiveness and frustrate users. Establishing a dedicated support team, promptly addressing technical issues, and providing clear channels for user feedback can help mitigate the impact of technical glitches and maintain user satisfaction.
8. Measuring ROI
- Unclear Benefits: Quantifying the return on investment (ROI) of new software can be challenging, especially in the short term. Setting clear objectives, defining measurable metrics, and regularly evaluating performance against benchmarks can provide insights into the software's impact on productivity, efficiency, and cost savings.
- Performance Metrics: Establishing the right metrics to measure the software's impact requires careful consideration of the company's goals and KPIs. Collaborating with stakeholders, conducting regular performance reviews, and adjusting metrics as needed can ensure accurate ROI assessment and continuous improvement.
9. Vendor Reliability
- Support and Service: Relying on the software vendor for ongoing support and updates means that any issues with the vendor can directly affect business operations. Choosing reputable vendors with a track record of reliability, responsive customer support, and transparent communication channels can mitigate risks and ensure a positive vendor-client relationship.
- Vendor Stability: Ensuring the long-term stability and reliability of the software provider is crucial to avoid disruptions. Conducting thorough vendor assessments, reviewing financial stability, and establishing contingency plans in case of vendor issues can safeguard against potential disruptions and ensure business continuity.
10. User Adoption and Engagement
- Engagement: Ensuring that all users actively engage with and utilize the software requires effective change management strategies and ongoing user support. Providing incentives, recognition for user contributions, and fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement can promote user engagement and maximize the software's value.
- Feedback Loop: Establishing a feedback loop to continuously improve the software based on user experiences and requirements is essential for long-term success. Encouraging open communication, actively soliciting user feedback, and prioritizing user-driven enhancements can enhance user satisfaction, drive adoption, and ensure the software remains aligned with business needs.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, adequate resource allocation, and a strategic approach to change management. By anticipating and mitigating these issues, service industry businesses can successfully adopt new software and realize its benefits.
Overcoming Challenges
Adopting software in the service industry can bring significant benefits, but it also comes with several challenges. Here are the major challenges:
1. Resistance to Change
- Communication and Transparency: In addition to explaining the benefits of the new software, ensure transparency throughout the implementation process. Keep employees informed about timelines, milestones, and any changes in plans. Encourage open dialogue and address questions or concerns promptly.
- Change Champions: Identify and empower change champions within the organization. These individuals can act as advocates for the new software, helping to build excitement, address concerns, and facilitate smooth adoption among their peers.
- Incentives and Recognition: Offer incentives or recognition programs to motivate employees to embrace the change. Recognize and reward early adopters or individuals who demonstrate proficiency in using the software, encouraging others to follow suit.
2. Training and Skill Gaps
- Role-Based Training: Customize training programs based on employees' roles and responsibilities. Provide targeted training modules that focus on the specific functionalities and workflows relevant to each job function.
- Hands-On Practice: Offer hands-on practice sessions where employees can interact with the software in a simulated environment. Encourage experimentation and exploration to build confidence and familiarity with the software.
- Peer Learning: Facilitate peer-to-peer learning opportunities where experienced users can mentor and support their colleagues. Pairing novice users with more experienced individuals can accelerate the learning process and foster collaboration.
3. Cost and Budget Constraints
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis: Consider the total cost of ownership over the software's lifecycle, including initial implementation costs, ongoing maintenance, and potential savings or revenue gains. Present a comprehensive TCO analysis to stakeholders to justify the investment.
- ROI Forecasting: Forecast the potential return on investment (ROI) of the software based on projected improvements in productivity, efficiency, and cost savings. Use historical data, benchmarks, and industry benchmarks to support ROI projections and demonstrate the software's financial benefits.
- Negotiation with Vendors: Negotiate with software vendors to explore flexible pricing options, discounts, or bundled packages that align with the company's budget constraints. Leverage competitive offers from other vendors to negotiate more favorable terms.
4. Integration Issues
- Pilot Testing: Conduct pilot testing or proof-of-concept trials to assess the software's compatibility with existing systems and identify any integration challenges early on. Use pilot results to refine integration strategies and address compatibility issues before full-scale implementation.
- API Documentation and Support: Work closely with software vendors to obtain comprehensive API documentation and technical support resources. Ensure that the software's APIs are well-documented and supported to facilitate smooth integration with third-party systems and tools.
- Interdepartmental Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT teams, departmental stakeholders, and software vendors to develop a cohesive integration plan. Encourage open communication and alignment of objectives to streamline integration efforts and minimize conflicts.
5. Data Security Concerns
- Security Audits and Assessments: Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and gaps in data security practices. Implement recommended security measures and protocols to strengthen data protection and mitigate security risks.
- Employee Training: Provide comprehensive training on data security best practices and protocols to all employees who will interact with the software. Emphasize the importance of safeguarding sensitive information and adhering to security policies and procedures.
- Compliance Monitoring: Establish processes for monitoring and ensuring compliance with relevant industry regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Regularly review and update security policies to align with evolving regulatory requirements and best practices.
6. Customization and Flexibility
- Requirements Gathering: Conduct thorough requirements gathering sessions with key stakeholders to identify and prioritize the company's unique needs and workflows. Document detailed requirements and use them to guide customization efforts and configuration settings.
- Agile Development Approach: Adopt an agile development approach to software customization, allowing for iterative development cycles and frequent feedback loops. Solicit feedback from end-users throughout the customization process to ensure that the software meets their needs and expectations.
- Vendor Collaboration: Collaborate closely with software vendors to explore customization options and develop tailored solutions. Leverage vendor expertise and industry best practices to implement customizations that optimize the software's functionality and usability for the company's specific requirements.
7. Downtime and Disruption
- Phased Rollout Strategy: Implement the software in phases or modules to minimize disruption to day-to-day operations. Start with a small pilot group or department and gradually expand the rollout as users become familiar with the software and any issues are addressed.
- Contingency Planning: Develop contingency plans and backup procedures to mitigate the impact of potential downtime or technical glitches during implementation. Identify key stakeholders and decision-makers responsible for addressing emergencies and ensure clear communication channels for reporting and resolving issues.
- User Support Resources: Provide dedicated user support resources, such as helpdesk support, knowledge bases, and online forums, to assist users during the implementation process. Empower users to troubleshoot common issues independently and escalate more complex problems to dedicated support teams for timely resolution.
8. Measuring ROI
- Benchmarking: Establish baseline metrics and benchmarks to measure the company's performance before implementing the software. Use these benchmarks to track and compare performance metrics over time, providing a clear basis for assessing the software's impact on productivity, efficiency, and cost savings.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Metrics: Utilize both qualitative and quantitative metrics to evaluate the software's ROI comprehensively. Quantitative metrics, such as cost savings or revenue growth, provide tangible evidence of financial benefits, while qualitative metrics, such as user satisfaction or process improvements, offer insights into intangible benefits.
- Regular Reviews and Reporting: Conduct regular reviews and reporting on key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress towards ROI goals. Present findings and insights to stakeholders through comprehensive reports and presentations, highlighting successes, areas for improvement, and actionable recommendations for maximizing ROI.
9. Vendor Reliability
- Vendor Due Diligence: Conduct thorough due diligence on potential software vendors to assess their reliability, reputation, and financial stability. Review vendor references, case studies, and customer testimonials to evaluate their track record of delivering quality products and services.
- Service-Level Agreements (SLAs): Negotiate clear and comprehensive SLAs with software vendors to establish expectations for support, maintenance, and service levels. Define metrics and performance targets for vendor performance and include provisions for penalties or remedies in case of non-compliance.
- Escalation Procedures: Establish escalation procedures and protocols for addressing issues or disputes with software vendors. Define clear lines of communication and escalation paths for resolving issues promptly and effectively, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations.
10. User Adoption and Engagement
- User-Centric Design: Prioritize user-centric design principles and usability testing to create an intuitive and engaging user experience. Solicit feedback from end-users throughout the software development process and incorporate user preferences and suggestions into the design.
- Change Management Communication: Develop a comprehensive change management communication plan to keep users informed and engaged throughout the implementation process. Provide regular updates, training sessions, and opportunities for feedback to ensure that users feel involved and supported.
- Gamification and Incentives: Implement gamification techniques and incentives to encourage user adoption and engagement with the software. Offer rewards, recognition, or incentives for achieving milestones, completing training modules, or providing valuable feedback, fostering a culture of participation and enthusiasm among users.
Future Trends
Future trends in workforce management software are shaped by technological advancements, evolving workplace dynamics, and changing employee expectations. Here are some key trends to watch for:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Predictive Analytics: AI and machine learning algorithms enable workforce management software to analyze historical data and predict future trends, such as staffing needs, employee turnover, and performance patterns.
- Smart Scheduling: AI-driven scheduling algorithms can optimize employee schedules based on factors like workload, availability, and skill sets, minimizing overstaffing, and reducing labor costs.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI-powered insights can provide personalized recommendations for career development, training opportunities, and performance improvement, tailored to each employee's unique strengths and goals.
2. Remote Work and Flexible Work Arrangements
- Remote Work Support: Workforce management software will increasingly focus on supporting remote and distributed teams, with features for virtual collaboration, remote attendance tracking, and performance management.
- Flexible Scheduling: Flexible scheduling tools will become more prevalent, allowing employees to set their own schedules based on preferences and priorities while still meeting business needs.
- Hybrid Work Models: Software solutions will adapt to hybrid work models, enabling seamless coordination between in-office and remote workers, and providing tools for managing hybrid schedules and workflows.
3. Employee Experience and Engagement
- Employee-Centric Design: Workforce management software will prioritize user experience, with intuitive interfaces, mobile-friendly designs, and customizable features that empower employees to manage their own schedules and tasks.
- Employee Feedback Mechanisms: Software platforms will incorporate tools for collecting real-time feedback from employees, enabling managers to gauge sentiment, address concerns, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
- Recognition and Rewards: Integrated recognition and rewards systems will become more common, allowing managers to acknowledge and reward employee achievements, milestones, and contributions directly within the software.
4. Automation and Robotics
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Workforce management software will leverage RPA to automate repetitive administrative tasks, such as data entry, payroll processing, and compliance reporting, freeing up time for HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants will provide employees with instant access to information and support, answering common questions, assisting with scheduling requests, and guiding users through self-service features.
- Workflow Automation: Advanced workflow automation capabilities will streamline business processes across the organization, from recruitment and onboarding to performance management and talent development.
5. Data Privacy and Security
- Enhanced Data Protection: With increased regulatory scrutiny and growing concerns about data privacy, workforce management software will incorporate stronger security measures, including encryption, access controls, and compliance monitoring.
- GDPR Compliance: Software vendors will prioritize GDPR compliance and data protection standards, ensuring that employee data is handled responsibly, with transparent consent mechanisms and robust data management practices.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Proactive cybersecurity measures, such as threat detection, intrusion prevention, and incident response protocols, will be integrated into workforce management software to safeguard against data breaches and cyberattacks.
6. Integration and Interoperability
- Unified Platforms: Workforce management software will move towards unified platforms that integrate seamlessly with other HR systems, such as payroll, talent management, and learning management systems, providing a holistic view of employee data and processes.
- API Ecosystems: Software vendors will expand their API ecosystems to facilitate integrations with third-party applications and services, allowing organizations to customize their workforce management solutions and extend functionality as needed.
- Interoperability Standards: Industry-wide interoperability standards will emerge to promote compatibility and data exchange between different software systems, reducing integration complexity and enhancing data interoperability.
7. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)
- DEI Analytics: Workforce management software will incorporate diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) analytics to track key metrics, such as representation, pay equity, and inclusion scores, enabling organizations to identify disparities and take proactive measures to address them.
- Inclusive Recruitment Tools: Software solutions will offer inclusive recruitment tools that help organizations attract diverse talent pools, mitigate bias in the hiring process, and foster a more inclusive workplace culture.
- Training and Development Programs: Workforce management platforms will support DEI initiatives by providing tools for designing and delivering inclusive training and development programs, fostering empathy, cultural competence, and allyship among employees.
8. Gig Workforce Management
- Gig Economy Integration: Workforce management software will adapt to the rise of the gig economy by incorporating features for managing freelance, contract, and contingent workers alongside traditional employees.
- On-Demand Scheduling: Platforms will offer on-demand scheduling capabilities that enable organizations to quickly deploy gig workers to meet fluctuating demand, leveraging AI-driven algorithms to match available workers with open shifts.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Software solutions will provide robust compliance and risk management features to ensure that organizations adhere to labor laws, tax regulations, and contractual obligations when engaging gig workers.
9. Skills-Based Workforce Management
- Skills Mapping and Gap Analysis: Workforce management software will include tools for mapping employee skills, assessing skill gaps, and aligning talent with project requirements and business objectives.
- Skills Development Plans: Platforms will support individualized skills development plans, recommending training opportunities, certifications, and learning pathways to help employees enhance their skills and advance their careers.
- Agile Talent Deployment: Organizations will adopt agile talent deployment strategies, leveraging workforce management software to quickly mobilize employees with the right skills for project-based work and cross-functional initiatives.
10. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Initiatives
- ESG Reporting: Workforce management software will incorporate features for tracking and reporting on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, such as carbon emissions, diversity metrics, and community impact, to support sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
- Employee Wellbeing Metrics: Platforms will measure and monitor employee wellbeing metrics, such as work-life balance, mental health, and job satisfaction, providing insights into the organization's social impact and commitment to employee welfare.
- ESG Compliance: Software solutions will help organizations ensure compliance with ESG regulations and standards, facilitating transparency, accountability, and ethical practices in workforce management and operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of workforce management software is poised to transform the way organizations manage their human capital, adapt to evolving workplace dynamics, and enhance employee experiences. With advancements in technology such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics, workforce management software will become more predictive, personalized, and efficient than ever before.
The trends outlined above indicate a shift towards more flexible, inclusive, and agile workforce management practices, accommodating remote work arrangements, gig economy participation, and skills-based talent deployment. Software solutions will prioritize user experience, data security, and interoperability, enabling seamless integration with other HR systems and third-party applications.
As organizations navigate the complexities of the modern workforce landscape, workforce management software will continue to evolve to meet their evolving needs and challenges. By embracing these future trends and leveraging innovative technologies, organizations can optimize their talent management processes, drive operational efficiency, and unlock new opportunities for growth and success in the digital age.